Extension Development
Gopeed supports extension development using JavaScript. Extensions can enhance Gopeed's functionality, such as downloading videos or music from a website. You can quickly learn more about it through the official examples.
Gopeed extensions are based on git to achieve decentralized extension management. As long as the extension source code is hosted in a remote git repository, it can be installed and updated through Gopeed. Therefore, whether it is github, gitee, gitlab, or other git hosting platforms, they can all be used as extension repositories.
Quick Start
Using scaffolding
Gopeed provides a scaffolding to help you quickly create an extension development project template:
npx create-gopeed-ext@latestnpx create-gopeed-ext@latestIn the creation process, you will see the following prompts:
√ Project name (gopeed-extension-demo) ...
√ Choose a template » Webpack
Success! Created gopeed-extension-demo at D:\code\study\js\gopeed-extension-demo
Inside that directory, you can run several commands:
git init
Initialize git repository
npm install
Install dependencies
npm run dev
Compiles and hot-reloads for development.
npm run build
Compiles and minifies for production.
We suggest that you begin by typing:
cd gopeed-extension-demo
Happy coding!√ Project name (gopeed-extension-demo) ...
√ Choose a template » Webpack
Success! Created gopeed-extension-demo at D:\code\study\js\gopeed-extension-demo
Inside that directory, you can run several commands:
git init
Initialize git repository
npm install
Install dependencies
npm run dev
Compiles and hot-reloads for development.
npm run build
Compiles and minifies for production.
We suggest that you begin by typing:
cd gopeed-extension-demo
Happy coding!Manual setup
If you are not familiar with the node.js peripheral tools, you can also manually create a project, the file structure is as follows:
├── index.js
├── manifest.json├── index.js
├── manifest.jsonLocal debugging
After the project is built, you need to do local debugging. You can install the local extension project into Gopeed for debugging. The specific steps are as follows:
- Enable the
Gopeeddeveloper mode, click the install button5 times in a rowon the extension page to enable the developer mode.
Click the button to select the extension directory in the directory selector to install.
If you use the
webpackmode in the scaffolding, you can start automatic compilation throughnpm run dev.Create a task to see the extension take effect.
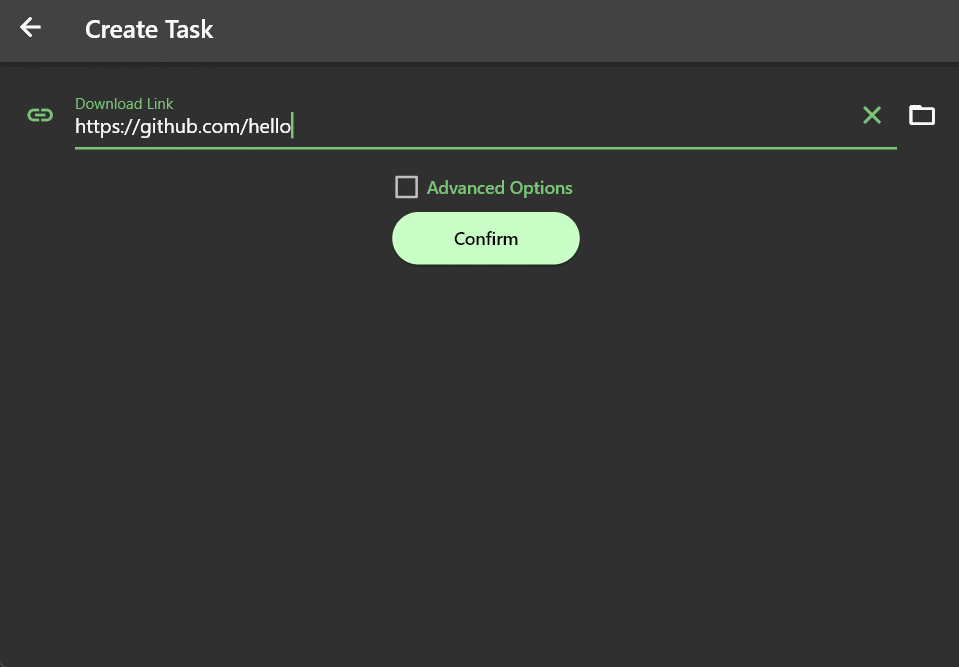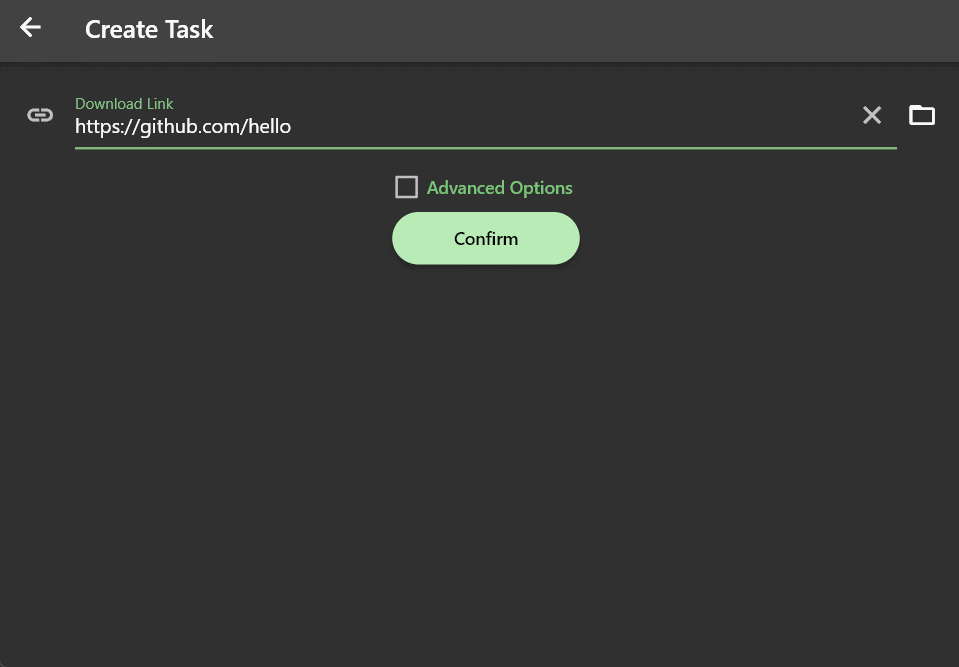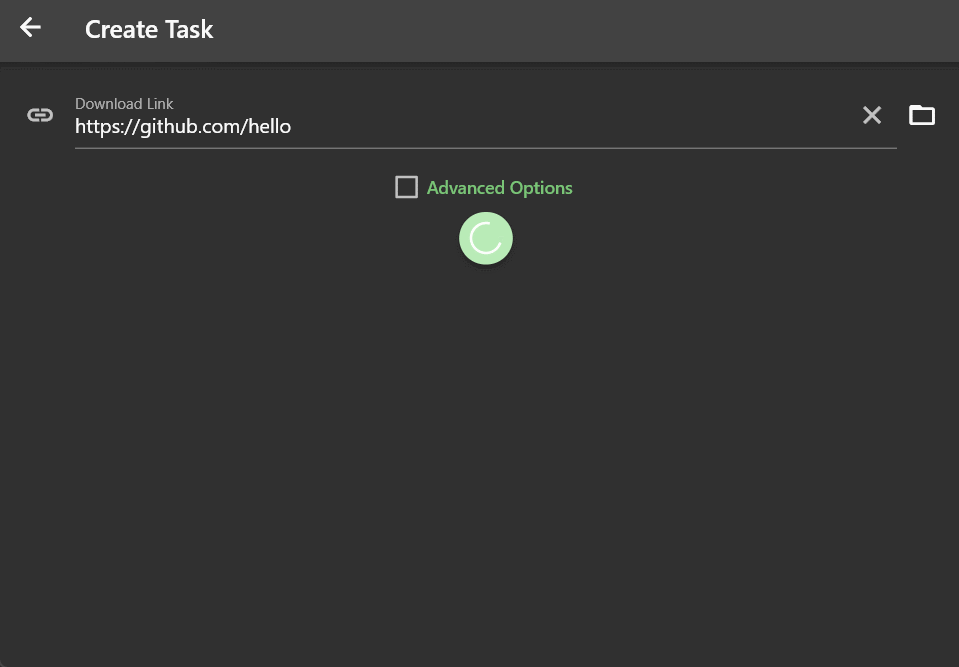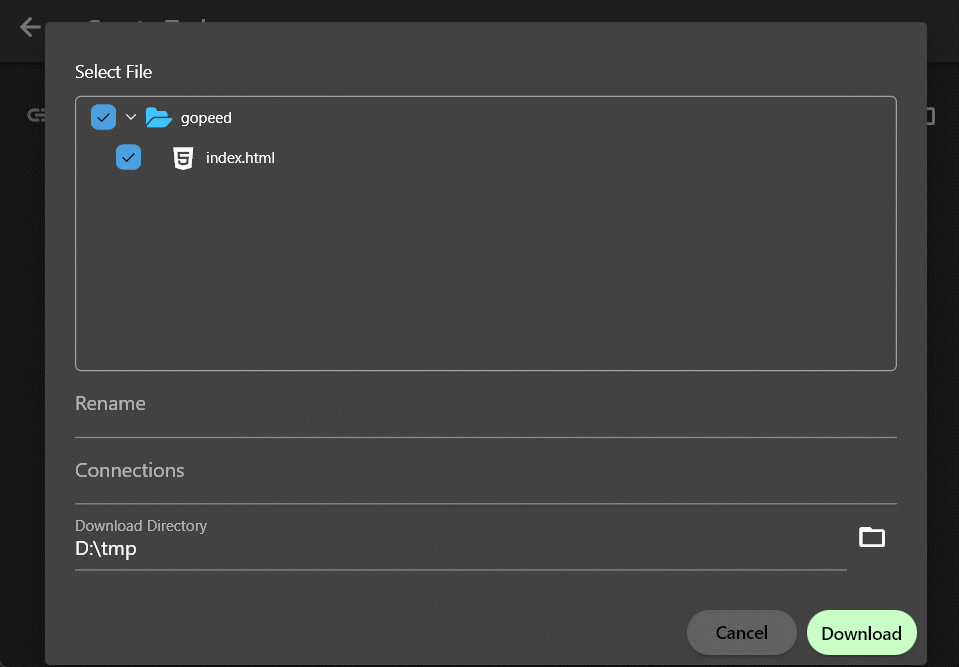
It can be seen that the example extension created through the scaffolding can parse an example/index.html file when creating a task using the https://github.com/hello link.
Note: Developer mode is only valid on the desktop platform.
Development explanation
In the previous section, we were able to create a basic extension and debug it locally, but what is happening under the hood?
First, let's take a look at the manifest.json file, which is the manifest file of the extension. It describes the information of the extension. Each extension project must contain a manifest.json file in the root directory. The sample file in this section is as follows:
{
"name": "gopeed-extention-demo",
"author": "",
"title": "gopeed extention demo title",
"description": "gopeed extention demo description",
"icon": "",
"version": "1.0.0",
"homepage": "",
"repository": {
"url": ""
},
"scripts": [
{
"event": "onResolve",
"match": {
"urls": ["*://github.com/*"]
},
"entry": "dist/index.js"
}
],
"settings": []
}{
"name": "gopeed-extention-demo",
"author": "",
"title": "gopeed extention demo title",
"description": "gopeed extention demo description",
"icon": "",
"version": "1.0.0",
"homepage": "",
"repository": {
"url": ""
},
"scripts": [
{
"event": "onResolve",
"match": {
"urls": ["*://github.com/*"]
},
"entry": "dist/index.js"
}
],
"settings": []
}Next, let's introduce the meaning of each field one by one:
nameandauthor: Gopeed will use<author>@<name>as the ID of the extension. After filling in theauthor, it can ensure that it is not easy to be overwritten and installed with other extensions, so it is strongly recommended to fill in theauthorfield.titleanddescription: The title and description of the extension.icon: Extension icon, fill in the relative path, for example:icon.png.version: Extension version, using semver specification, when the extension is updated, it is compared based on this field, so please make sure that the version number is in compliance with the specification.homepage: Extension homepage, for example:https://gopeed.com.repository: The git repository address to which the extension belongs. Gopeed extensions rely ongitto achieve decentralized extension management. Therefore, if your extension needs to be installed and updated by users, you must host the extension source code in a remote git repository and configure this field.For example:
json{ "url": "https://github.com/gopeed/gopeed-extension-demo" }{ "url": "https://github.com/gopeed/gopeed-extension-demo" }If a git repository contains multiple extension projects, you can specify a subdirectory through the
directoryattribute, for example:json{ "url": "https://github.com/GopeedLab/gopeed-extension-samples", "directory": "github-contributor-avatars-sample" }{ "url": "https://github.com/GopeedLab/gopeed-extension-samples", "directory": "github-contributor-avatars-sample" }In Gopeed installation, you need to use
#to separate, e.g.https://github.com/GopeedLab/gopeed-extension-samples#github-contributor-avatars-sample.scripts:Pay attention!This is the configuration of the Gopeed extension activation event.The
onResolveevent configured in the sample project will be triggered when parsing tasks. Thematch.urlsfield is used to match the URL created by the task. If the match is successful, the script file specified in theentryfield will be executed. In the example of the scaffolding project above, it is configured to match*://github.com/*and then run thedist/index.jsfile. Therefore, when we enter ahttps://github.com/hellolink, it is matched and then triggers the execution of the extension script. The content of the script will be explained in detail later.The matching rules are consistent with the matching rules of Chrome extensions, which can be referred to here
Currently, the extension only supports the
onResolveactivation event, and more events will be supported in the future.settings: Extension settings, through the configuration declaration, the corresponding settings page can be generated in Gopeed to provide user-defined settings, such as customCookie, customUser-Agent, etc., for example:json[ { "name": "cookie", "title": "网站 Cookie", "description": "Cookie 可以通过浏览器开发者工具获取", "type": "string" }, { "name": "quality", "title": "默认画质", "type": "number", "value": "1080", "options": [ { "label": "1080P", "value": "1080" }, { "label": "720P", "value": "720" }, { "label": "480P", "value": "480" } ] } ][ { "name": "cookie", "title": "网站 Cookie", "description": "Cookie 可以通过浏览器开发者工具获取", "type": "string" }, { "name": "quality", "title": "默认画质", "type": "number", "value": "1080", "options": [ { "label": "1080P", "value": "1080" }, { "label": "720P", "value": "720" }, { "label": "480P", "value": "480" } ] } ]name: Setting item name, required.title: Setting item title, required.description: Setting item description, optional.type: Setting item type, optional values:string,number,boolean.value: Setting item default value, optional.
Script writing
In the previous section, we have learned how to configure the manifest, and now let's introduce how to write the extension script.
Runtime environment
Gopeed extension script engine is implemented by goja which is a JavaScript interpreter written in pure Go. However, since goja is only a pure js runtime, the APIs of browser and node.js are not supported. Currently, Gopeed implements XMLHttpRequest and fetch APIs, which means you can use these two APIs or third-party libraries based on them to implement network requests, such as axios, superagent, etc.
Another thing to note is that goja natively supports most of the es6+ syntax, but a few syntaxes are not supported, such as async generator, but it doesn't matter, the project created by the scaffolding has been configured with bable, you can use the latest es syntax happily, and the script will eventually be compiled into es5 syntax.
Demo script explanation
When an event is triggered, the script file specified in the entry field will be executed. The script file in the sample project is as follows:
gopeed.events.onResolve((ctx) => {
ctx.res = {
name: "example",
files: [
{
name: "index.html",
req: {
url: "https://example.com",
},
},
],
};
});gopeed.events.onResolve((ctx) => {
ctx.res = {
name: "example",
files: [
{
name: "index.html",
req: {
url: "https://example.com",
},
},
],
};
});Next, let's introduce the meaning of each field one by one:
gopeed.events.onResolve: Here, theonResolveevent is registered, and the method inside is the specific logic of the extension.ctx: Event context, which contains some information about the current event. In theonResolveevent,ctxcontains the following fields:req: Request information, including the url and headers of the resource.res: Response information, the script needs to assign the parsed file list toctx.res, and Gopeed will download according to the file list returned in it.
In short, it is necessary to parse the list of files that need to be downloaded based on the request information in ctx.req in the onResolve callback function and assign it to ctx.res. The script above is easy to understand. It parses an index.html file and its corresponding download address, and then assigns it to ctx.res.
About
ctx's detailed explanation can be found in documentation.
Extension settings
For the sake of making the extension more dynamic, Gopeed provides a set of standard configuration items. By declaring the settings attribute, the corresponding extension settings page can be generated in Gopeed to provide user-defined settings, such as custom Cookie, custom User-Agent, etc., for example:
{
"settings": [
{
"name": "cookie",
"title": "网站 Cookie",
"description": "Cookie 可以通过浏览器开发者工具获取",
"type": "string"
},
{
"name": "quality",
"title": "默认画质",
"type": "number",
"value": "1080",
"options": [
{
"label": "1080P",
"value": "1080"
},
{
"label": "720P",
"value": "720"
},
{
"label": "480P",
"value": "480"
}
]
}
]
}{
"settings": [
{
"name": "cookie",
"title": "网站 Cookie",
"description": "Cookie 可以通过浏览器开发者工具获取",
"type": "string"
},
{
"name": "quality",
"title": "默认画质",
"type": "number",
"value": "1080",
"options": [
{
"label": "1080P",
"value": "1080"
},
{
"label": "720P",
"value": "720"
},
{
"label": "480P",
"value": "480"
}
]
}
]
}This declares two setting items, one is cookie, the other is quality, let's take a look at their effects:
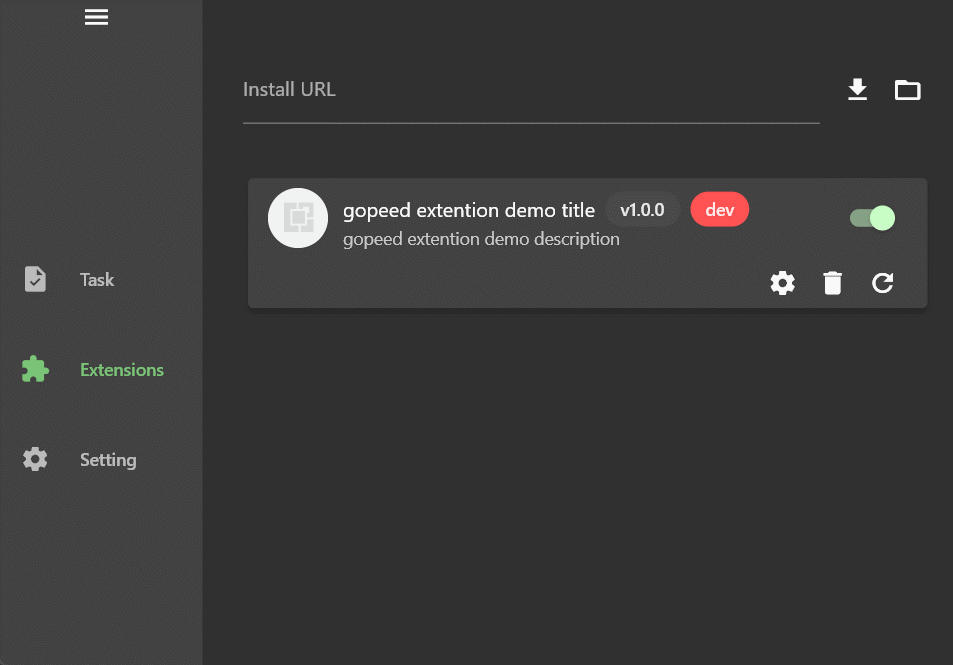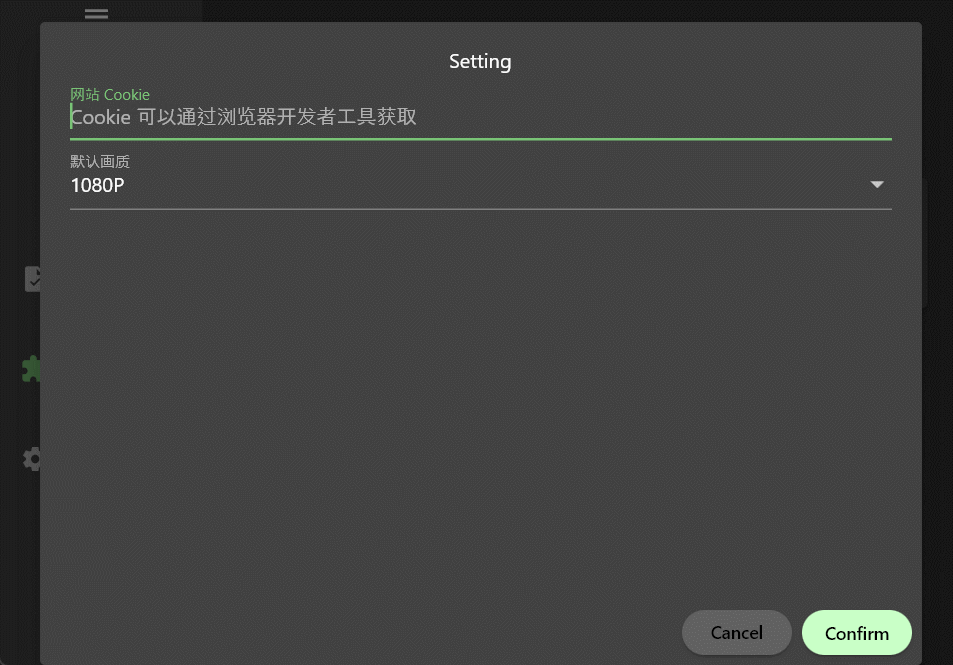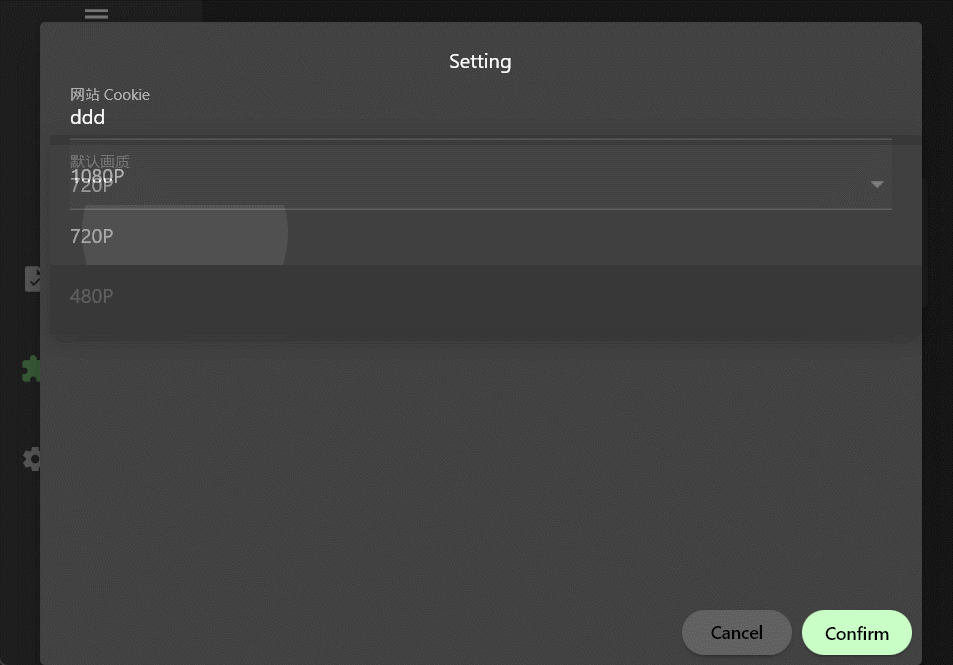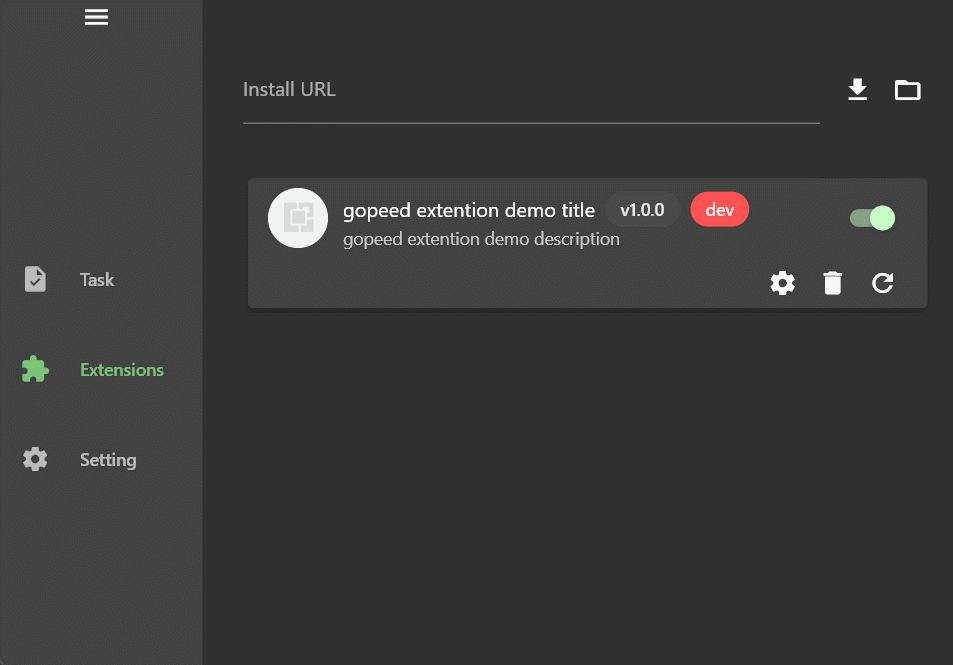
Cookie is an input box, and quality is a drop-down box. It should be noted that the type field determines the type of the setting item. Currently, three types are supported:
stringnumberboolean
If the options option is configured, it will be rendered as a drop-down box for users to choose.
Then you can get the value of the setting through gopeed.settings in the extension script, for example:
gopeed.events.onResolve((ctx) => {
// Access cookie setting
console.log(gopeed.settings.cookie);
// Access quality setting
console.log(gopeed.settings.quality);
});gopeed.events.onResolve((ctx) => {
// Access cookie setting
console.log(gopeed.settings.cookie);
// Access quality setting
console.log(gopeed.settings.quality);
});Extension storage
Gopeed provides a set of storage APIs to support extension persistence storage of data such as login token, for example:
gopeed.events.onResolve((ctx) => {
// Get the token, if it not exists, then login
const token = gopeed.storage.get("token");
if(!token){
const token = await login();
gopeed.storage.set("token",token)
}
// Then do something with the token
// ...
});gopeed.events.onResolve((ctx) => {
// Get the token, if it not exists, then login
const token = gopeed.storage.get("token");
if(!token){
const token = await login();
gopeed.storage.set("token",token)
}
// Then do something with the token
// ...
});Note: For detailed API, please refer to documentation.
Extension debugging
In the script, you can output logs through the gopeed.logger object, which supports three levels: debug, info, warn, error, for example:
gopeed.logger.debug("debug");
gopeed.logger.info("info");
gopeed.logger.warn("warn");
gopeed.logger.error("error");gopeed.logger.debug("debug");
gopeed.logger.info("info");
gopeed.logger.warn("warn");
gopeed.logger.error("error");Log files are in the logs directory in the Gopeed installation directory, and the file name is extension.log, which can be viewed in real time through the tail -f extension.log command.
Note: The debug level log is only valid in the extension installed in developer mode.
Extension publishing
When the extension development is completed, if it is a webpack project created by the scaffolding, you need to compile it:
npm run buildnpm run buildThen we need to create a remote repository, for example, create a https://github.com/xxx/gopeed-extension-demo repository on github, and then modify the repository field in manifest.json accordingly:
{
"repository": {
"url": "https://github.com/xxx/gopeed-extension-demo"
}
}{
"repository": {
"url": "https://github.com/xxx/gopeed-extension-demo"
}
}Correctly configuring
repositorycan allow the extension to obtain remote update capabilities. If the extension is a subdirectory under the git repository, you can specify the subdirectory through thedirectoryattribute, for example:json{ "repository": { "url": "https://github.com/xxx/gopeed-extension-demo", "directory": "path" } }{ "repository": { "url": "https://github.com/xxx/gopeed-extension-demo", "directory": "path" } }
After that, remember to configure the author and name fields of the extension to reduce the risk of duplicate names with other extensions.
Finally, push the project to the remote repository to complete the release. In order to make it easier for users to search for Gopeed extensions on github, it is recommended that the project name be uniformly prefixed with gopeed-extension-, for example, gopeed-extension-demo, and add the gopeed-extension tag to the project on github.
Extension installation
After publishing to the remote repository, you can install it in Gopeed. Open the extension page, enter the git clone address of the extension's HTTP protocol (you can omit the .git suffix at the end), and click the Install button to install it.
Note: If the extension directory is a subdirectory, you need to add
#after the address, and then add the subdirectory name, for examplehttps://github.com/xxx/gopeed-extension-demo#path.
Official examples
The official provides two representative sample extensions for reference, which are:
github-contributor-avatars-sample
This extension is a project that depends on node.js and is suitable for complex development requirements. It uses the cheerio library to parse webpage DOM to obtain the list of files that need to be downloaded.
This extension is a
pure jsproject without any dependencies, suitable for simple development requirements. It usesfetchto implement network requests to obtain the list of files that need to be downloaded.
 Gopeed Docs
Gopeed Docs